With the release of iOS 11 this year, Apple released many new frameworks and Vision framework is one of them. Vision framework enables app developers to implement any task that involves computer vision without even detailed knowledge of the subject. This includes facial analysis (smile, frown etc), bar-code detection, scene image classification, object detection, tracking etc.
In this post we will focus our efforts in scene text recognition. Scene text is text that can appear anywhere in environment like signs, store fronts, notice boards etc. There are two parts of it, first scene text detection and second is scene text recognition. Detection is, as the name implies, to find if there is any text present in image and recognition is, what actually is written in that text. Our app should be able to recognize text with varying conditions and it does not depends on a particular font, text size or color.
Project Setup
For this tutorial, we need Xcode 9.0 and an iPhone or iPad running iOS 11. As of writing, both Xcode 9.0 and iOS 11 are in beta.
Launch Xcode 9.0 and click on Create a new project, select iOS tab and choose Single View App. Hit Next and enter product name (I have used SceneTextRecognitioniOS), in language option select Swift and save the project in some directory.
Hit Command + R to run the app, it will compile and you will see a white screen.
Create a new swift file and name it Preview.swift and write the code mentioned below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
import UIKit import AVFoundation class PreviewView: UIView { var videoPreviewLayer: AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer { guard let layer = layer as? AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer else { fatalError("Expected `AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer` type for layer. Check PreviewView.layerClass implementation.") } return layer } var session: AVCaptureSession? { get { return videoPreviewLayer.session } set { videoPreviewLayer.session = newValue } } // MARK: UIView override class var layerClass: AnyClass { return AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer.self } } |
Please note, this view is using AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer as a backing layer.
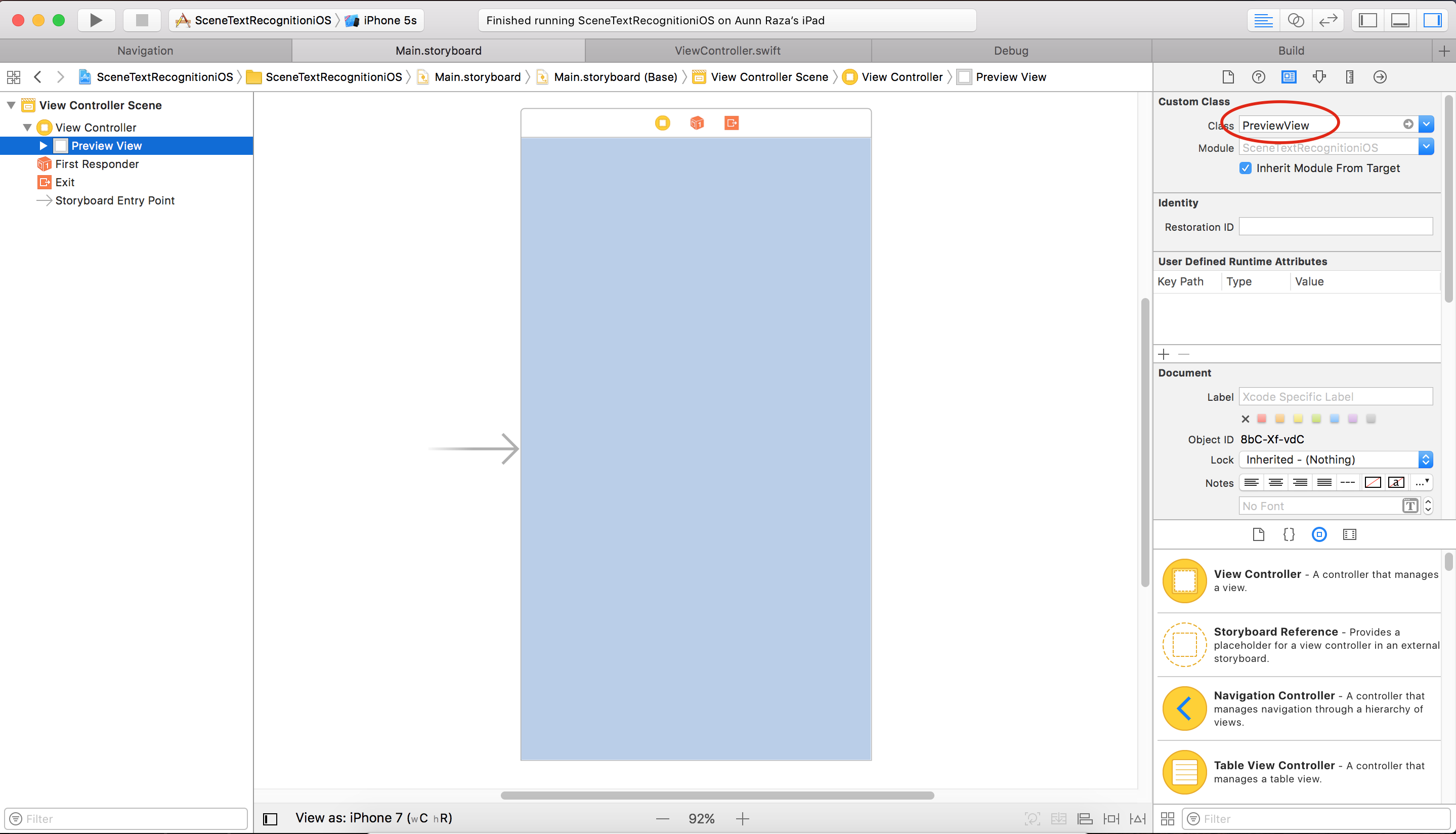
Open Main.storyboard and click on View Controller Scene, expand it and select View of ViewController. From utilities pane, select identity inspector and set class field to PreviewView (you should see auto complete if everything goes well).
Open Info.plist file and add Privacy - Camera Usage Description key with value Recognize Scene Text. Also add Vision framework to your project.
Below is the complete ViewController.swift file.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 |
import AVFoundation import UIKit import Vision class ViewController: UIViewController { override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() // Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib. if isAuthorized() { configureTextDetection() configureCamera() } } override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() { super.didReceiveMemoryWarning() // Dispose of any resources that can be recreated. } private func configureTextDetection() { textDetectionRequest = VNDetectTextRectanglesRequest(completionHandler: handleDetection) textDetectionRequest!.reportCharacterBoxes = true } private func configureCamera() { preview.session = session let cameraDevices = AVCaptureDevice.DiscoverySession(deviceTypes: [.builtInWideAngleCamera], mediaType: AVMediaType.video, position: .back) var cameraDevice: AVCaptureDevice? for device in cameraDevices.devices { if device.position == .back { cameraDevice = device break } } do { let captureDeviceInput = try AVCaptureDeviceInput(device: cameraDevice!) if session.canAddInput(captureDeviceInput) { session.addInput(captureDeviceInput) } } catch { print("Error occured \(error)") return } session.sessionPreset = .high let videoDataOutput = AVCaptureVideoDataOutput() videoDataOutput.setSampleBufferDelegate(self, queue: DispatchQueue(label: "Buffer Queue", qos: .userInteractive, attributes: .concurrent, autoreleaseFrequency: .inherit, target: nil)) if session.canAddOutput(videoDataOutput) { session.addOutput(videoDataOutput) } preview.videoPreviewLayer.videoGravity = .resize session.startRunning() } private func handleDetection(request: VNRequest, error: Error?) { guard let detectionResults = request.results else { print("No detection results") return } let textResults = detectionResults.map() { return $0 as? VNTextObservation } if textResults.isEmpty { return } DispatchQueue.main.async { self.view.layer.sublayers?.removeSubrange(1...) let viewWidth = self.view.frame.size.width let viewHeight = self.view.frame.size.height for textResult in textResults { guard let rects = region.characterBoxes else { return } var xMin = CGFloat.greatestFiniteMagnitude var xMax: CGFloat = 0 var yMin = CGFloat.greatestFiniteMagnitude var yMax: CGFloat = 0 for rect in rects { xMin = min(xMin, rect.bottomLeft.x) xMax = max(xMax, rect.bottomRight.x) yMin = min(yMin, rect.bottomRight.y) yMax = max(yMax, rect.topRight.y) } let x = xMin * viewWidth let y = (1 - yMax) * viewHeight let width = (xMax - xMin) * viewWidth let height = (yMax - yMin) * viewHeight let layer = CALayer() layer.frame = CGRect(x: x, y: y, width: width, height: height) layer.borderWidth = 2 layer.borderColor = UIColor.red.cgColor view.layer.addSublayer(layer) } } } private var preview: PreviewView { return view as! PreviewView } private func isAuthorized() -> Bool { let authorizationStatus = AVCaptureDevice.authorizationStatus(for: AVMediaType.video) switch authorizationStatus { case .notDetermined: AVCaptureDevice.requestAccess(for: AVMediaType.video, completionHandler: { (granted:Bool) -> Void in if granted { DispatchQueue.main.async { self.configureCamera() self.configureTextDetection() } } }) return true case .authorized: return true case .denied, .restricted: return false } } private var textDetectionRequest: VNDetectTextRectanglesRequest? private let session = AVCaptureSession() } extension ViewController: AVCaptureVideoDataOutputSampleBufferDelegate { // MARK: - Camera Delegate and Setup func captureOutput(_ output: AVCaptureOutput, didOutput sampleBuffer: CMSampleBuffer, from connection: AVCaptureConnection) { guard let pixelBuffer = CMSampleBufferGetImageBuffer(sampleBuffer) else { return } var imageRequestOptions = [VNImageOption: Any]() if let cameraData = CMGetAttachment(sampleBuffer, kCMSampleBufferAttachmentKey_CameraIntrinsicMatrix, nil) { imageRequestOptions[.cameraIntrinsics] = cameraData } let imageRequestHandler = VNImageRequestHandler(cvPixelBuffer: pixelBuffer, orientation: CGImagePropertyOrientation(rawValue: 6)!, options: imageRequestOptions) do { try imageRequestHandler.perform([textDetectionRequest!]) } catch { print("Error occured \(error)") } } } |
In configureTextDetection method, we are creating a text detection request. In configureCamera method we are setting current session to our preview layer. Then we iterate through available cameras and pick the one that is on the back side and can capture video. After that we add this to our session. Next we create a video output capture, set its delegate and dispatch queue to use and add it to session. Finally, we start the session to run.
Another important method to consider is handleDetection. Here we are dealing with the detection results coming from vision framework. We are extracting the detected text regions and draw a bounding box around them on screen.
captureOutput(:didOutput:from) is method where we receive the camera stream and forward it to our text detection request.
Now run this code on your iOS device, point your camera at any text available nearby and you will see rectangles drawn around detected text.
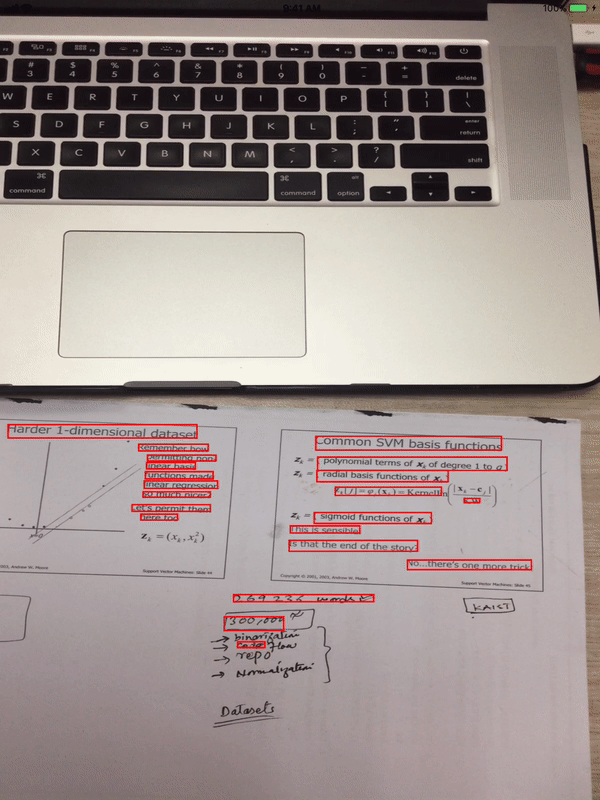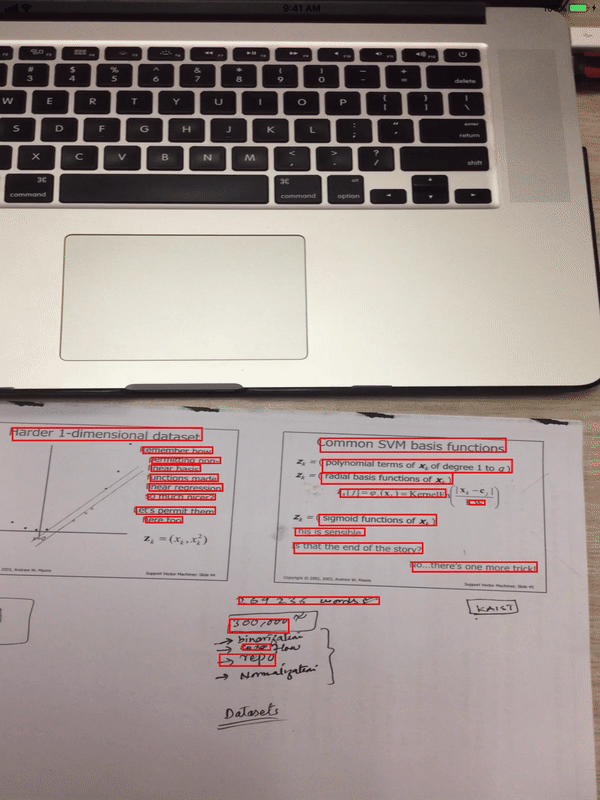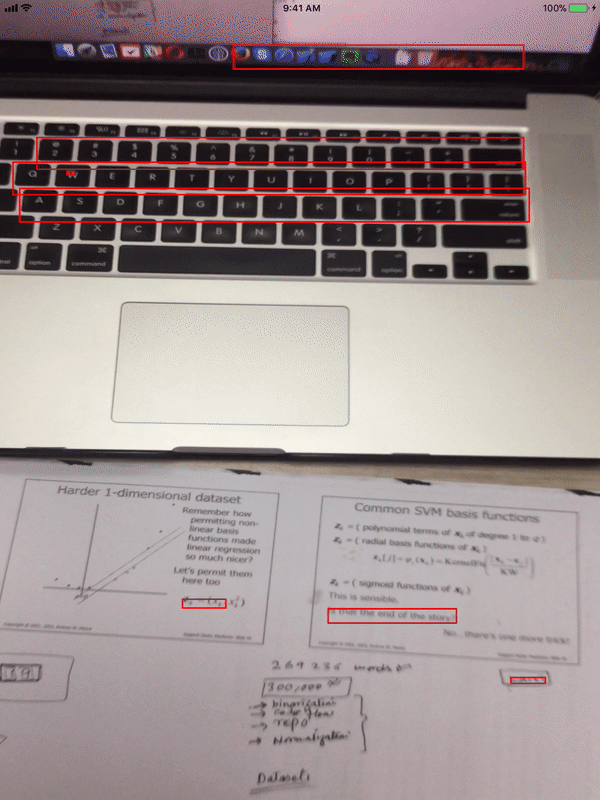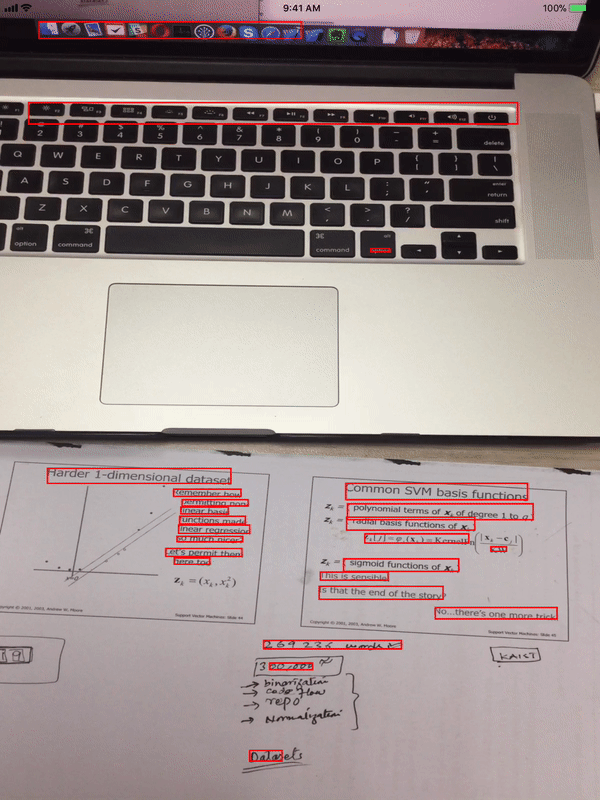
Text Recognition
Now lets head over to text recognition. For this we will use Tesseract. Tesseract is an open source and most widely used OCR (Optical Character Recognition) engine that is used by many researchers and industrial products. For iOS we will use tesseract for iOS. Please download a zip file from here (taken from Raywenderlich Tesseract OCR Tutorial which can be found here ). Extract the zip and it contains TesseractOCR.framework and tessdata folder. Drag and drop TesseractOCR.framework from finder into your Xcode project. In Xcode, click on project file, select your app target, select Build Phases from top option, in Link Binary With Libraries and click + and select TesseractOCR.framework which we just added to project. Also add CoreImage.framework in Link Binary With Libraries, this framework is part of iOS SDK. Also add libstdc++.6.0.9.dylib or libstdc++.6.0.9.tbd, if libstdc++.6.0.9.dylib is not available.
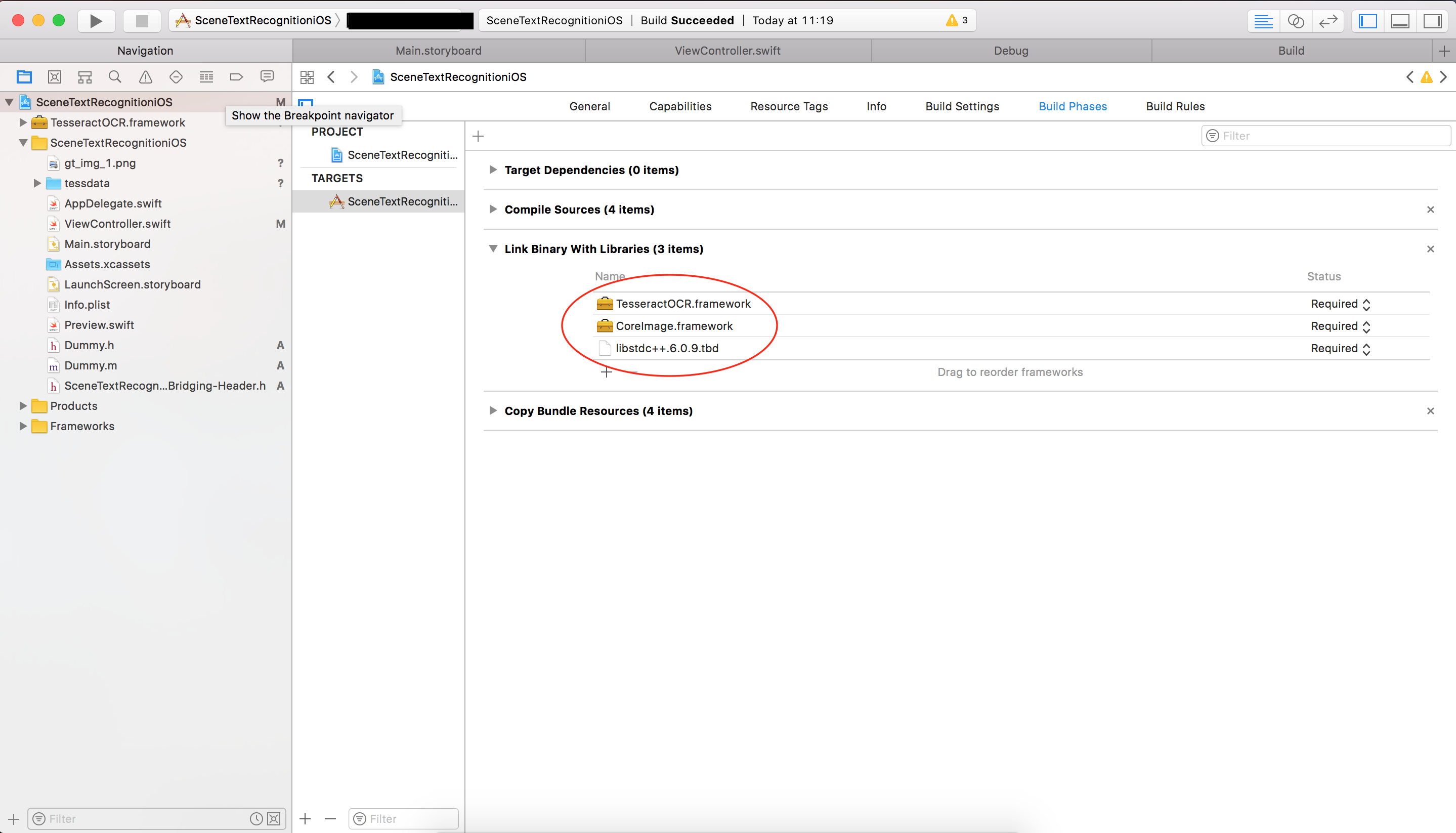
Click Build Settings, find Other Linker Flags and append -lstdc++
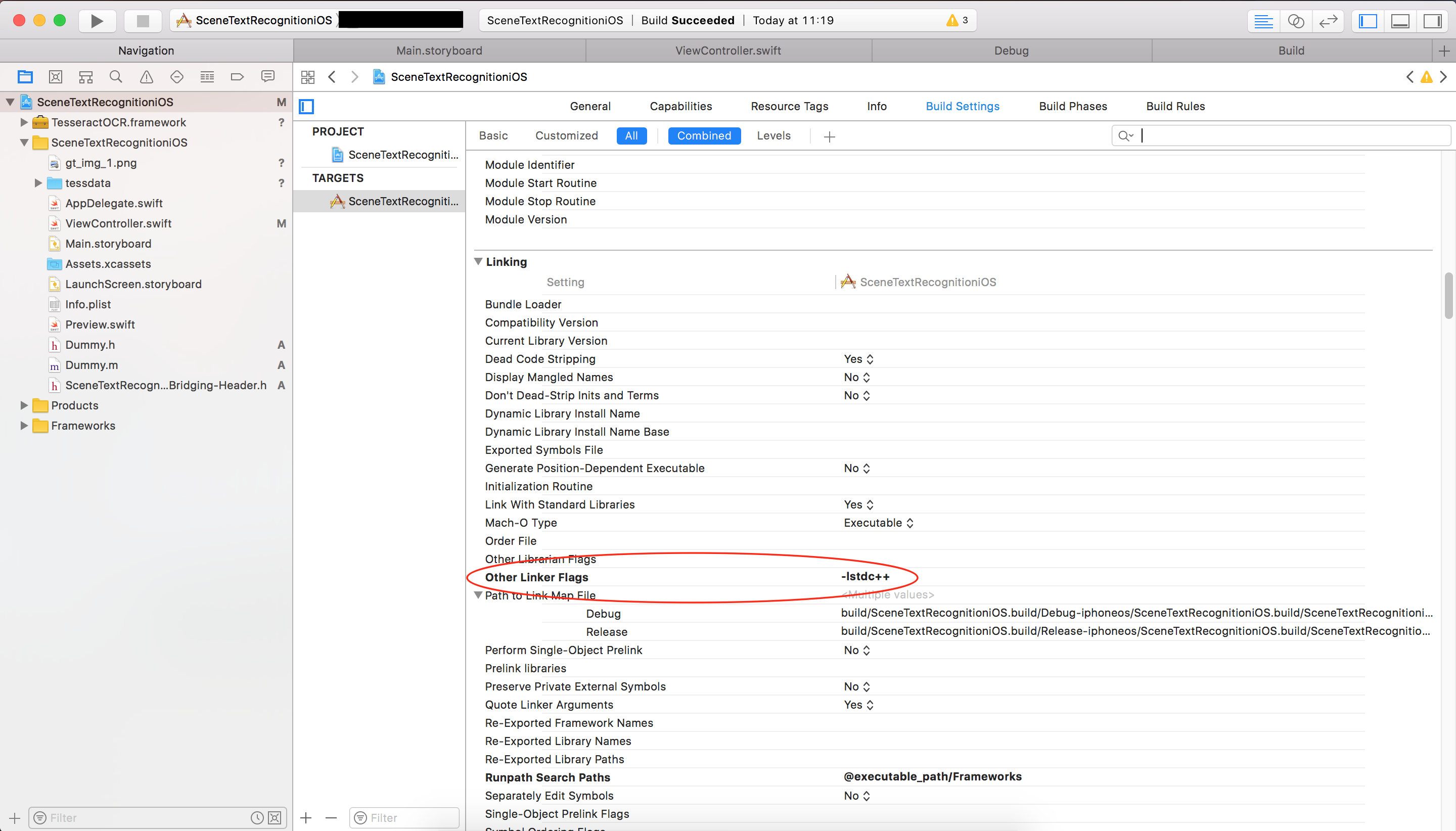
Find Enable Bitcode and set its value to No(Bitcode is part of Apple thinning process. What it does is generate an intermediate representation of compiled code. If an app is upload on App store with bitcode enabled, at install time Apple will make some optimisation on the fly for that target user device. More info on bitcode here)
Tesseract needs some more files in order to run properly. There is a folder inside zip named tessdata, which is also needed to make sure it is included in your project. Unfortunately due to some unavoidable reasons this cannot be done in a straight forward manner in Xcode 9. Below are the steps that are needed to be performed in order to make tessdata available properly in project.
In XCode 9, Reference folder is not automatically supported. To use it, follow these steps (These are taken from GitHub):
- Create a
tessdatafolder into the project folder (open the project folder on Finder and create thetessdatafolder at the same level of theAppDelegate.swiftfile). Do not add this folder into the XCode project. - Add your Tesseract trained data files into the
tessdatafolder. - Right click on YourProject.xcodeproj and click on
Show Package Contents - Double click on
project.pbxproj(open it with XCode) - Add into the /* Begin PBXBuildFile section */:
64E9ADE81F2A2436007BAC6F /* tessdata in Resources */ = {isa = PBXBuildFile; fileRef = 64E9ADE71F2A2436007BAC6F /* tessdata */; };
- Add into the /* Begin PBXFileReference section */:
64E9ADE71F2A2436007BAC6F /* tessdata */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; lastKnownFileType = folder; path = tessdata; sourceTree = ""; };
- Add into the /* Begin PBXGroup section */, at the same level of the AppDelegate.swift`:
64E9ADE71F2A2436007BAC6F /* tessdata */,
- Add into the /* Begin PBXResourcesBuildPhase section */, at the same level of the
Main.storyboard in Resources:
64E9ADE81F2A2436007BAC6F /* tessdata in Resources */,
- Save the file
- Open the project in XCode 9
Since Tesseract for iOS is developed with Objective-C ,we need Objective-C bridging header to use in our swift app. The best way to add bridging header and all associated project settings is to add a Objective-C file to the project. Create a new file and name it as Dummy and remember to select language to Objective-C. A prompt will appear that says Would you like to configure an Objective-C bridging header? Select Yes
Add below line to bridging header:
#import <TesseractOCR/TesseractOCR.h>
Add the below mentioned two instance variables in ViewController class:
|
1 2 |
private var textObservations = [VNTextObservation]() private var tesseract = G8Tesseract(language: "eng", engineMode: .tesseractOnly) |
In the first line, we are creating a VNTextObservation array to cache results from detection. Next, we are creating a tesseract object. This will be used for text recognition. In handleDetection method add textObservations = textResults as! [VNTextObservation], just above DispatchQueue.main.async line. Below is the updated handleDetection method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
private func handleDetection(request: VNRequest, error: Error?) { guard let detectionResults = request.results else { print("No detection results") return } let textResults = detectionResults.map() { return $0 as? VNTextObservation } if textResults.isEmpty { return } textObservations = textResults as! [VNTextObservation] DispatchQueue.main.async { guard let sublayers = self.view.layer.sublayers else { return } for layer in sublayers[1...] { if (layer as? CATextLayer) == nil { layer.removeFromSuperlayer() } } let viewWidth = self.view.frame.size.width let viewHeight = self.view.frame.size.height for result in textResults { if let textResult = result { let layer = CALayer() var rect = textResult.boundingBox rect.origin.x *= viewWidth rect.size.height *= viewHeight rect.origin.y = ((1 - rect.origin.y) * viewHeight) - rect.size.height rect.size.width *= viewWidth layer.frame = rect layer.borderWidth = 2 layer.borderColor = UIColor.red.cgColor self.view.layer.addSublayer(layer) } } } } |
One thing to note in the above method is, previously we were removing all sub-layers and now we are removing all those layers which are not CATextLayer. The reason is that we will be adding many CATextLayer object once we got something in text recognition.
Now lets go to actual work of recognition. Open up captureOutput method and in the end, we will be doing recognition through tesseract.
The idea is, we will crop the image at the position where text is detected, given that cropped image to tesseract for recognition and show the results we got from tesseract on screen. Note that we may get many regions in image where text is detected.
Below is the complete implementation of captureOutput method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 |
func captureOutput(_ output: AVCaptureOutput, didOutput sampleBuffer: CMSampleBuffer, from connection: AVCaptureConnection) { guard let pixelBuffer = CMSampleBufferGetImageBuffer(sampleBuffer) else { return } var imageRequestOptions = [VNImageOption: Any]() if let cameraData = CMGetAttachment(sampleBuffer, kCMSampleBufferAttachmentKey_CameraIntrinsicMatrix, nil) { imageRequestOptions[.cameraIntrinsics] = cameraData } let imageRequestHandler = VNImageRequestHandler(cvPixelBuffer: pixelBuffer, orientation: CGImagePropertyOrientation(rawValue: 6)!, options: imageRequestOptions) do { try imageRequestHandler.perform([textDetectionRequest!]) } catch { print("Error occured \(error)") } var ciImage = CIImage(cvPixelBuffer: pixelBuffer) let transform = ciImage.orientationTransform(for: CGImagePropertyOrientation(rawValue: 6)!) ciImage = ciImage.transformed(by: transform) let size = ciImage.extent.size var recognizedTextPositionTuples = [(rect: CGRect, text: String)]() for textObservation in textObservations { guard let rects = textObservation.characterBoxes else { continue } var xMin = CGFloat.greatestFiniteMagnitude var xMax: CGFloat = 0 var yMin = CGFloat.greatestFiniteMagnitude var yMax: CGFloat = 0 for rect in rects { xMin = min(xMin, rect.bottomLeft.x) xMax = max(xMax, rect.bottomRight.x) yMin = min(yMin, rect.bottomRight.y) yMax = max(yMax, rect.topRight.y) } let imageRect = CGRect(x: xMin * size.width, y: yMin * size.height, width: (xMax - xMin) * size.width, height: (yMax - yMin) * size.height) let context = CIContext(options: nil) guard let cgImage = context.createCGImage(ciImage, from: imageRect) else { continue } let uiImage = UIImage(cgImage: cgImage) tesseract?.image = uiImage tesseract?.recognize() guard var text = tesseract?.recognizedText else { continue } text = text.trimmingCharacters(in: CharacterSet.newlines) if !text.isEmpty { let x = xMin let y = 1 - yMax let width = xMax - xMin let height = yMax - yMin recognizedTextPositionTuples.append((rect: CGRect(x: x, y: y, width: width, height: height), text: text)) } } textObservations.removeAll() DispatchQueue.main.async { let viewWidth = self.view.frame.size.width let viewHeight = self.view.frame.size.height guard let sublayers = self.view.layer.sublayers else { return } for layer in sublayers[1...] { if let _ = layer as? CATextLayer { layer.removeFromSuperlayer() } } for tuple in recognizedTextPositionTuples { let textLayer = CATextLayer() textLayer.backgroundColor = UIColor.clear.cgColor var rect = tuple.rect rect.origin.x *= viewWidth rect.size.width *= viewWidth rect.origin.y *= viewHeight rect.size.height *= viewHeight textLayer.frame = rect textLayer.string = tuple.text textLayer.foregroundColor = UIColor.green.cgColor self.view.layer.addSublayer(textLayer) } } } |
At line 11, try imageRequestHandler.perform([textDetectionRequest!]). This is a synchronous call, it performs the text detection and calls our detection handler method handleDetection. In this method, we store the detection observations in textObservations instance variable. At line 16, we create a CIImage from the current pixel buffer, calculate the appropriate transform for image at line 17 and then perform the transform at line 18. Next, we iterate through all the elements of textObservations. From the start of loop till line 41, we crop from original image and only get the cropped image where we have text detection available. At 42, we give that cropped image to tesseract to call its recognize method. Tesseract sometime appends new line character at the end of detected text, so we are removing new line characters at line 47. Next we adjust the position of detected text and add it to a rect/text tuple array. At line 56 we make sure to empty textObservations as it might end up being used if no text is detected in next frame. We dispatch in main queue, first remove all the existing text layers and then add new text layers for new recognized text.
The whole running project can be downloaded from here. Enjoy text recognition in iOS 11 and let me know about if you have any questions.

